The Place of Extended Reality in Digital Transformation Strategy for Manufacturing: Use Cases and Benefits
This article focuses on extended reality as one of the critical technologies the leading industry players leverage to enhance, automate, and modernize their business processes.
Growing Role of Extended Reality in Manufacturing
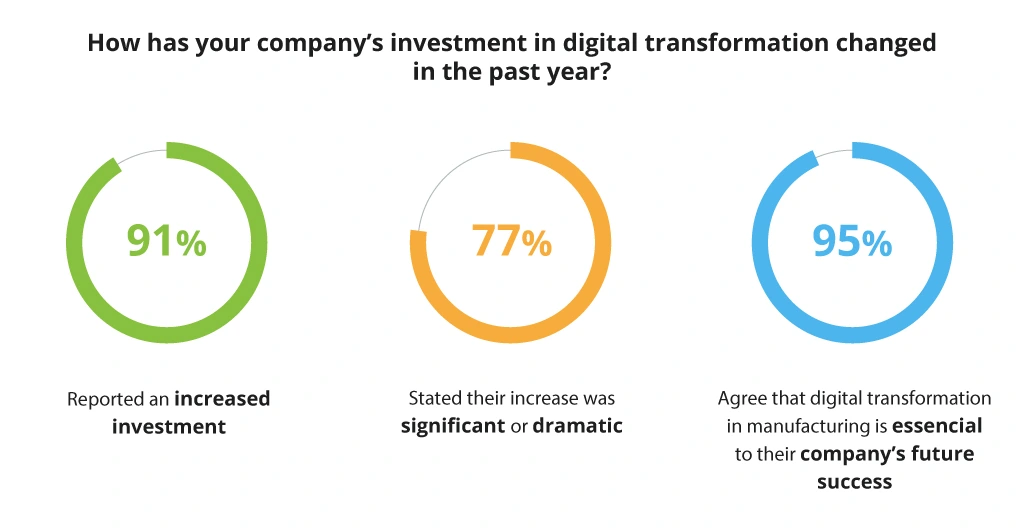
It’s safe to say that the massive adoption of innovative technologies in manufacturing is closely associated with the COVID-19 pandemic. The 2021 State of Manufacturing Report indicates that 95% of companies considered the pandemic to have a long-term impact on their business, which, in turn, provided a welcome boost to Industry 4.0.
Along with advanced data analytics, IoT, AI, ML, and robotics, extended reality (XR) is one of the most promising directions of digital transformation in manufacturing: 91% of companies increased their digital transformation investment in 2020, opting for XR as one of the value-driving solutions.
The Rise in Digital Transformation Investment
What is extended reality? Extended reality technology is a blanket term covering three different types of computer-generated simulations: virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR). The latter differ by their “virtuality” levels and are a mix of real and virtual environments, created with 3D modeling and accessed using dedicated wearables.
Although the concept of extended reality is nothing new — it was first introduced back in 1968 — it started gaining traction approximately ten years ago, expanding beyond gaming to healthcare, banking, architecture and construction, gas and oil, and automotive industries.
Benefits of Extended Reality in Manufacturing
The widespread adoption of XR in manufacturing is perfectly justified by the enormous advantages it can bring. So, what is the potential benefit of applying extended reality solutions?
Operations Optimization
The use of extended reality allows businesses to cut down on both time and money significantly while streamlining their essential operations. For example, Boeing uses AR lenses that decrease the cognitive load of employees when assembling an aircraft. Each Boeing has 130 miles of internal wires, and until recently, engineers had to check them by constantly shifting attention to paper documents packed with diagrams and schemes. Implementing AR allowed Boeing to switch from the cross-checking method to line-of-sight instructions, which resulted in minimizing the risk of mistakes and decreasing the wire assembly time by 25%.
Improved Collaboration
Extended reality helps successfully address the challenges of the remote work mode. It enables efficient real-time collaboration between the manufacturing specialists regardless of their location. XR solutions allow teams to exchange their experiences in virtual environments and get instant advice in case of a manufacturing line breakdown.
So how does it work in practice? For instance, at the Mercedes-Benz dealerships, technicians who need help can wear the HoloLens 2 headsets overlaying a mixed reality environment atop their field of view. They are then linked with remote Mercedes-Benz specialists who can see what the technicians observe and communicate with them in real-time. As a result, the on-site technicians get quick answers to maintenance questions, which allows them to work more productively.
Advanced Training Opportunities
Extended reality allows for placing new staff members in training situations that closely simulate work processes, helping them develop skills before going onto the production floor. In addition, with immersive training, subject matter experts can easily create step-by-step digital instructions overlaid upon real-world equipment. This inevitably translates into more efficient training processes and helps minimize training costs.
For example, Infopulse has developed an immersive educational platform for a global automotive manufacturer that includes a library of custom interactive training scenarios. The solution significantly reduced costs by replacing training facilities and props with their digital twins and eliminated the need to travel by enabling instant cooperation from any location. Moreover, the VR-powered education contributed to the employees’ safety during COVID.
Enhanced Quality of Products
The 2021 State of Manufacturing Report stated that quality issues caused cost overruns for 81% of respondents in 2020. Extended reality comes to save the day, effectively tackling the challenges of remote work and the lack of in-house experts. Innovative XR tools allow engineers to view systems through headsets and identify issues from a distance.
Better Safety
While employee safety is a crucial part of any business, it is of even greater importance for manufacturing. Fair enough, since many working environments suggest using potentially dangerous equipment. With XR applications, inexperienced staff members can be trained in low-risk environments, minimizing the chances of injury.
Quicker Time to Market
Virtual reality can help significantly reduce the time between the product design and its commercial production by replacing the time-consuming physical prototyping with interactive virtual models. Digital twins are more accessible to modify than physical models. They are also more straightforward to share, meaning faster and more efficient decision-making process and quicker time to market.
For instance, Watermark Products, an agency designing and manufacturing onboard products for airlines, was looking for a solution to tackle the challenge of the substantial time and cost involved in producing prototypes to test new designs. Today, the company uses Manufacturing AR to effectively bridge the gap between what is on screen and the actual outcome. With the help of Augment’s Solidworks plugin, they can easily visualize mock-ups and validate sizing for their products.
Extended Reality in Manufacturing: 5 Use Cases to Get You Inspired
1. Lloyd's Register Case: Exceptional Training Experiences
Extended reality fosters creating highly-efficient and safe learning environments, accessible from any corner of the globe. Statista predicts that by 2024, $4.1 billion will be invested in training with the help of augmented and virtual reality.
Lloyd’s Register provides professional assistance with safety and business operations to the energy industry players, educating clients on using the equipment being one of the company’s key offerings. A downturn in the market motivated Lloyd’s Register to find innovative ways to maintain its market share. The company was looking for a solution that would help strengthen the knowledge received during the training session, simulate real-life situations, and allow them to train people outside their facility in Houston and thus expand their business.
To accomplish these tasks, the company used AR and VR. A gamified virtual reality safety simulator was designed to reproduce situations where lives are at risk unless you take the right action. The adoption of XR helped Lloyd’s Register multiply their training bookings and increase ROI by three times.
2. L’Oréal Case: Streamlined Installation and Maintenance of Equipment
Extended reality empowers manufacturers to collaborate effectively with remote experts and use interactive knowledge repositories for prompt troubleshooting, which results in greater efficiency and lower service costs.
L’Oréal produces a variety of goods that call for sophisticated manufacturing equipment, which, in turn, requires proper installation and servicing. Having experts travel to the site involves costs and almost always means manufacturing delays.
The best approach to tackle this challenge was to find a way to leverage the expertise of external specialists. For this, the company chose Microsoft Dynamics 365 Remote Assist on HoloLens 2. It allows staff members in one location to watch the personnel in another place in real-time. They can react to the same image, use mixed-reality annotations, and see instructions in their real-world view. What is more, HoloLens 2 headset enables manipulating digital objects with fingers. As a result, L’Oréal managed to significantly cut down on costs, stepping up their manufacturing efficiency.
3. Airbus Case: Mixed Reality Bringing Design and Manufacturing to the Next Level
Mixed reality helps transform digital data into a three-dimensional experience by using holograms. Coupled with artificial intelligence and state-of-the-art hardware design, MR allows users to interact with holograms in a physical environment, either separately or in combination with real physical items.
Airbus, a pioneering manufacturer of aircraft and satellites, assigned mixed reality a special role in their digital transformation strategy. The company chose Microsoft’s Azure Mixed Reality and HoloLens 2 to speed up the design and production of aircraft while boosting safety and functionality.
With mixed reality, Airbus designers can virtually test their designs to ensure they are ready for manufacture. In addition, thanks to overlaying instructions or diagrams on a real piece of equipment, MR allows the production line personnel to easily access important information with their hands free. These mixed-reality solutions have helped Airbus designers to accelerate their design and manufacturing processes while enhancing quality greatly.
4. SEACOMP Case: Building Customer Trust Remotely
By simulating reality, XR technologies help businesses vividly demonstrate products and their features and collect valuable feedback before the product is launched, avoiding mistakes and gaining insights into customer needs.
SEACOMP is a global electronics manufacturer that supplies manufacturing solutions for customers across various industries globally. The company closely collaborates with the clients in product development, pointing out that this partnership is all about trust. Before the pandemic, SEACOMP built trust with its open-door policy, welcoming customers to visit their facilities, meet the team, and see their processes firsthand.
However, this became impossible with the coronavirus outbreak, making SEACOMP seek a safe, accurate, and immersive alternative to on-site visits. The company chose Matterport as its innovation partner. With the help of Matterport Capture Services and Matterport Capture Technician, they created digital twins of their facilities. This enabled their clients to experience 3D walkthroughs of the factory’s equipment and layout, saving time and cost and eliminating health risks.
According to Terry Arbaugh, the SEACOMP Vice President of Sales and Marketing, digital twins save nearly $250,000 in travel expenses annually for employees and customers. Also, this technology helps the company convert prospects into customers earlier in the sales cycle.
5. Ford Case: VR for Effective Collaboration and Human-Centric Designs
Automotive has been among the most enthusiastic adopters of XR technology. Prototype testing, creating high-grade navigation systems, and VR-powered self-driving cars are the industry's most common extended reality applications. However, XR is effectively used behind the scenes as well.
One of Ford’s digital transformation journey directions was enhancing collaborative efforts when designing vehicles. Ford is the first automaker to work with Gravity Sketch, a VR tool enabling designers to create more human-centric designs. Using headsets and operating controllers, Ford designers use gestures to sketch a virtual car, which can be rotated and viewed from any angle, even inside. The Co-Creation feature empowers multiple designers to engage in virtual model creation and make real-time adjustments, reducing the need for travel during the design phase.
As a result, Ford designers can work on the project virtually from anywhere and at any time, in the most convenient way, resulting in greater productivity. In addition, virtual models help Ford cut down on design time from weeks to hours without compromising on quality.
Conclusion
With the enormous advantages of extended reality for business, this innovative technology is definitely here to stay and amaze the world with even more impressive use cases. XR is one of the most value-driving opportunities for the manufacturing industry, opening a way for lower cost and risk, improved employee safety and collaboration, insightful data management, and novel marketing solutions.
Tap into the massive potential of extended reality to get a competitive edge and align with the companies prioritizing digital transformation over outdated manufacturing practices. At Infopulse, we are always eager to share our XR development best practices to create advanced digital solutions for businesses and help them grow.
![Extended Reality for Manufacturing [banner]](https://www.infopulse.com/uploads/media/the-place-of-extended-reality-1920x528.webp)

![CX with Virtual Assistants in Telecom [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/280x222-how-to-improve-cx-in-telecom-with-virtual-assistants.webp)
![How to Build Enterprise Software Systems [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-how-to-build-enterprise-software-systems.webp)
![Super Apps Review [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-introducing-Super-App-a-Better-Approach-to-All-in-One-Experience.webp)
![IoT Energy Management Solutions [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-iot-energy-management-benefits-use-сases-and-сhallenges.webp)

![5G Network Holes [Thumbnail]](/uploads/media/280x222-how-to-detect-and-predict-5g-network-coverage-holes.webp)
![How to Reduce Churn in Telecom [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-how-to-reduce-churn-in-telecom-6-practical-strategies-for-telco-managers.webp)
![White-label Mobile Banking App [Thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-white-label-mobile-banking-application.webp)
![Money20/20 Key Points [thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-humanizing-the-fintech-industry-money-20-20-takeaways.webp)
![Deepfake Detection [Thumbnail]](/uploads/media/thumbnail-280x222-what-is-deepfake-detection-in-banking-and-its-role-in-anti-money-laundering.webp)